Article updated on: September 23, 2025
Different therapeutic cells are used depending on the patient’s condition and treatment goals. These include stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), cord-derived MSCs, progenitor cells, or differentiated cells. By carefully selecting and delivering these cells, clinicians can support tissue repair, tissue regeneration, immune modulation, and even anti-inflammatory effects—core mechanisms detailed in the clinic’s treatment protocol
How Cell Therapy Works
Cell transplantation involves injecting, grafting, or implanting living cells to achieve a therapeutic effect. Examples include T-cell therapy for cancer treatment (immunotherapy) or stem cell therapy to regenerate diseased tissues.
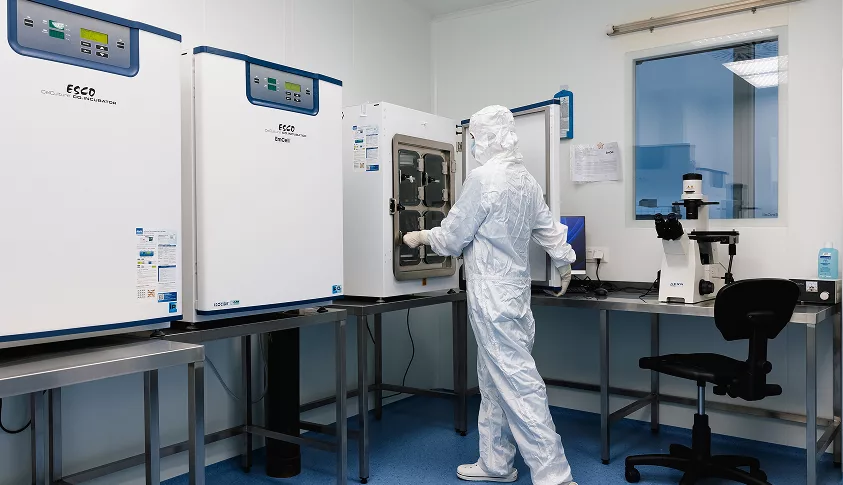
The field requires a deep understanding of cell biology, cell viability, and the precise techniques for cell harvesting, manipulation, and transplantation. Continuous clinical trials and research ensure safety and efficacy, while ethical sourcing and adherence to GMP and scientific standards - explained in the clinic’s science section - maintain the highest levels of patient care.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell (MSC) Therapy
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), particularly cord-derived MSCs, are key in regenerative medicine. They can differentiate into multiple cell types, supporting tissue repair, immune modulation, and anti-inflammatory processes. MSCs are used to treat degenerative diseases, autoimmune conditions, and support anti-aging and rejuvenation.

Benefits of MSC Therapy:
- Anti-Aging & Rejuvenation: Reduces inflammation, promotes tissue repair, and improves overall vitality.
- Degenerative Disease Management: Supports tissue regeneration and regulates immune responses in conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Safe and Effective: Delivered through non-invasive procedures outlined in the clinic’s treatment process to maximize cell viability and therapeutic absorption.
- Patient-Centered: Enables personalized medicine, improving quality of life, symptom management, and treatment outcomes.
Clinical Research and Protocols
Ongoing clinical trials confirm the efficacy and safety of cord-derived MSC therapy. Rigorous treatment protocols ensure that therapeutic cells maintain high viability and effectiveness, producing reliable patient outcomes backed by scientific evidence from the science section.
Patient Outcomes
Patients undergoing MSC therapy often experience:
- Enhanced energy and well-being
- Improved quality of life
- Long-lasting benefits in tissue repair, immune modulation, and symptom management
Success rates are high, with many patients showing sustained improvements over time, reflecting the therapy’s potential for healing and rejuvenation.
The Evolution of Cell Therapy
The concept of cell therapy dates back to the 19th century. Early experiments evolved into bone marrow transplantation, now a standard treatment for patients with compromised marrow due to disease, chemotherapy, or radiation.
Modern research focuses on stem cells—including embryonic, adult, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)—to advance cellular therapy and tissue regeneration. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and other therapeutic cells have become essential in treating degenerative diseases, autoimmune disorders, and aging-related conditions. For broader scientific insights, see the clinic’s articles such as The Future of Stem Cell Therapy.